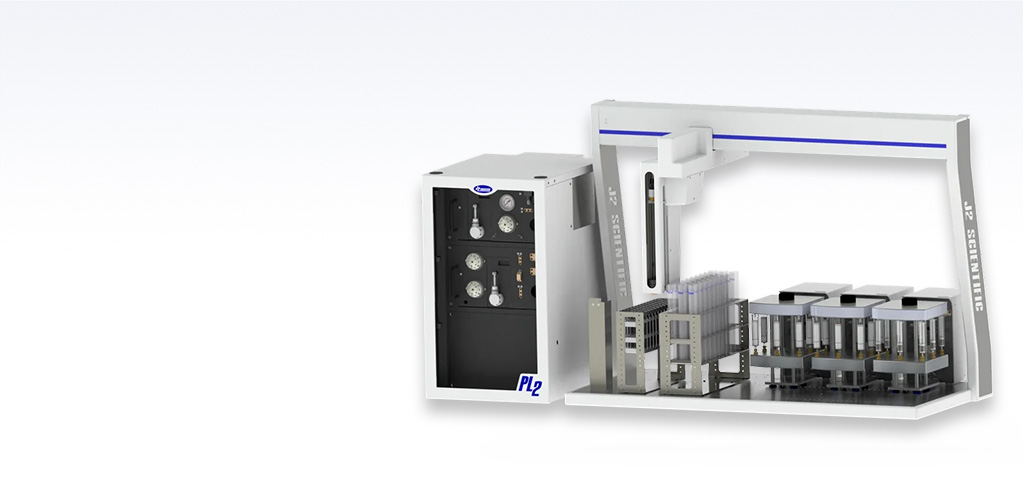
The PrepLinc SPEi Solid Phase Extraction Modules accentuates the line of full-featured automated sample preparation instruments. The SPEi system uses positive pressure for consistent flow sample to sample and run to run. The intuitive software and range of parameters make method development easy. Converting any manual SPE method to automated takes minimal time and effort.
Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) Module
The SPEi Inline Solid Phase Extraction Kit adapts to columns from 1mL to 15mL. It is ideal for sample and elution volumes up to 50 mL. Each column module holds 9 columns and the system can accomodate up to 5 column modules.
The LVi Large Volume Injection SPE Kit is optimized for SPE extractions on large volume samples. Specialized SPE column modules accommodate water extraction discs, as well as, standard SPE columns. The precision of the LVi pump module gives the necessary control of sample introduction to the extraction media and lets you choose priorities for flow vs. pressure. When combined with an optional standard column module, secondary cleanup or drying steps can be performed.

- Add up to 5 SPEi column modules
- Capacity of 45 samples
- Flow from one module to any other module
- Add column modules as need increases
- Solvent selector valve for selection of up to 12 solvents
SPE Module standout features
- Use cartridges from 1mL - 15mL plus many specialty and flash chromatography columns
- Perform multi-column procedures; up to 5 columns inline
- Flow Inject Module for water/aqueous samples
- Concentrate eluate to final volume or concentrate between prep processes with our AccuVap
- Ability to perform forward and reverse elution through cartridges
- Program up to 12 different solvents in a method
- Programmable flow rates to 50 mLs/min
- Positive Pressure Elution for Sample and Solvents
- Nitrogene Drying
- Select from 12 Solvents for processing (3 standard)
- Closed System with Pressure Monitoring
SPE Method Editor
Create simple, single-column or complex, multi-column methods through the same intuitive method editor. Fully automated sample prep for production labs.
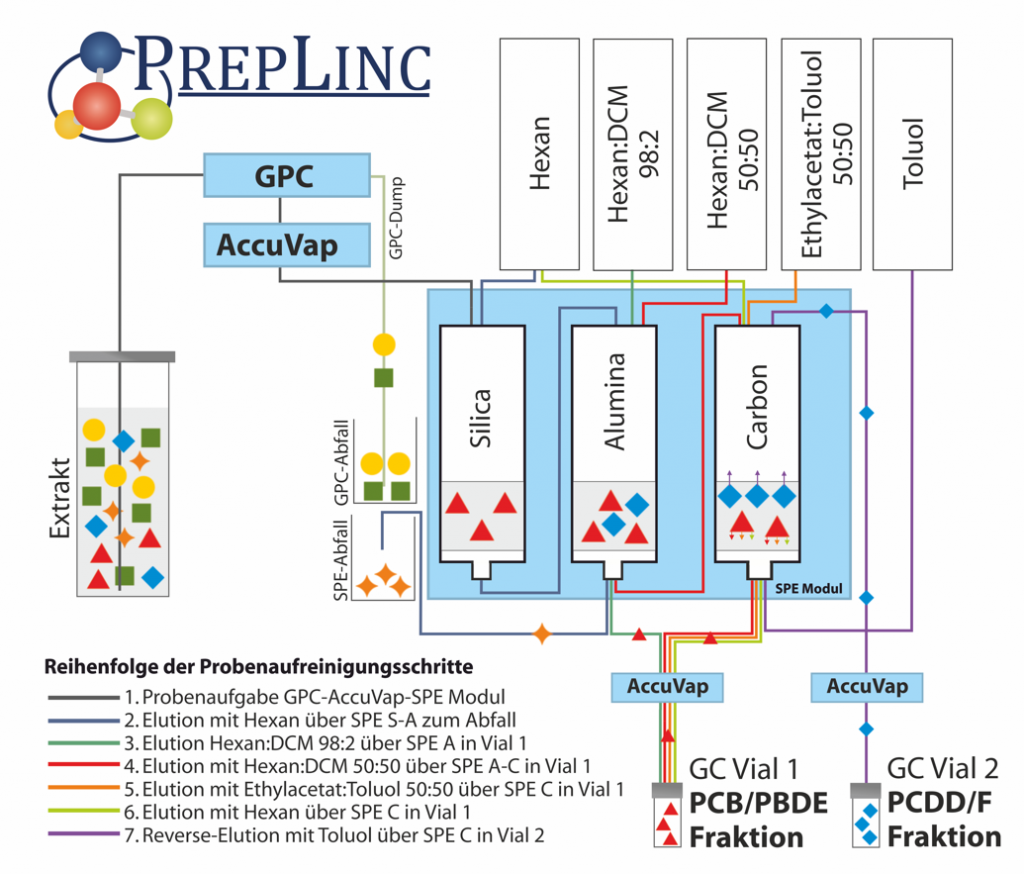
PrepLinc automates complex SPE applications where several different SPE cartridges are in use. The application example shows the clean up of a dioxin sample containing PCBs, PBDEs and PCDD/Fs cleaned up by GPC with evaporation and three different SPE cartridges.
PrepLinc Sequence Editor
• Sequences are not limited to one method, one module or one “Linc” method
• User can customize sequence as laboratory fl ow dictates
• Choose sample and collect tray and location for fi rst sample; sequentially copies for additional samples, but can be edited for unique situations
• Choose priority samples
• Re-arrange, add and delete unprocessed samples after run has begun
• Change method and tray information for unprocessed samples after run has begun
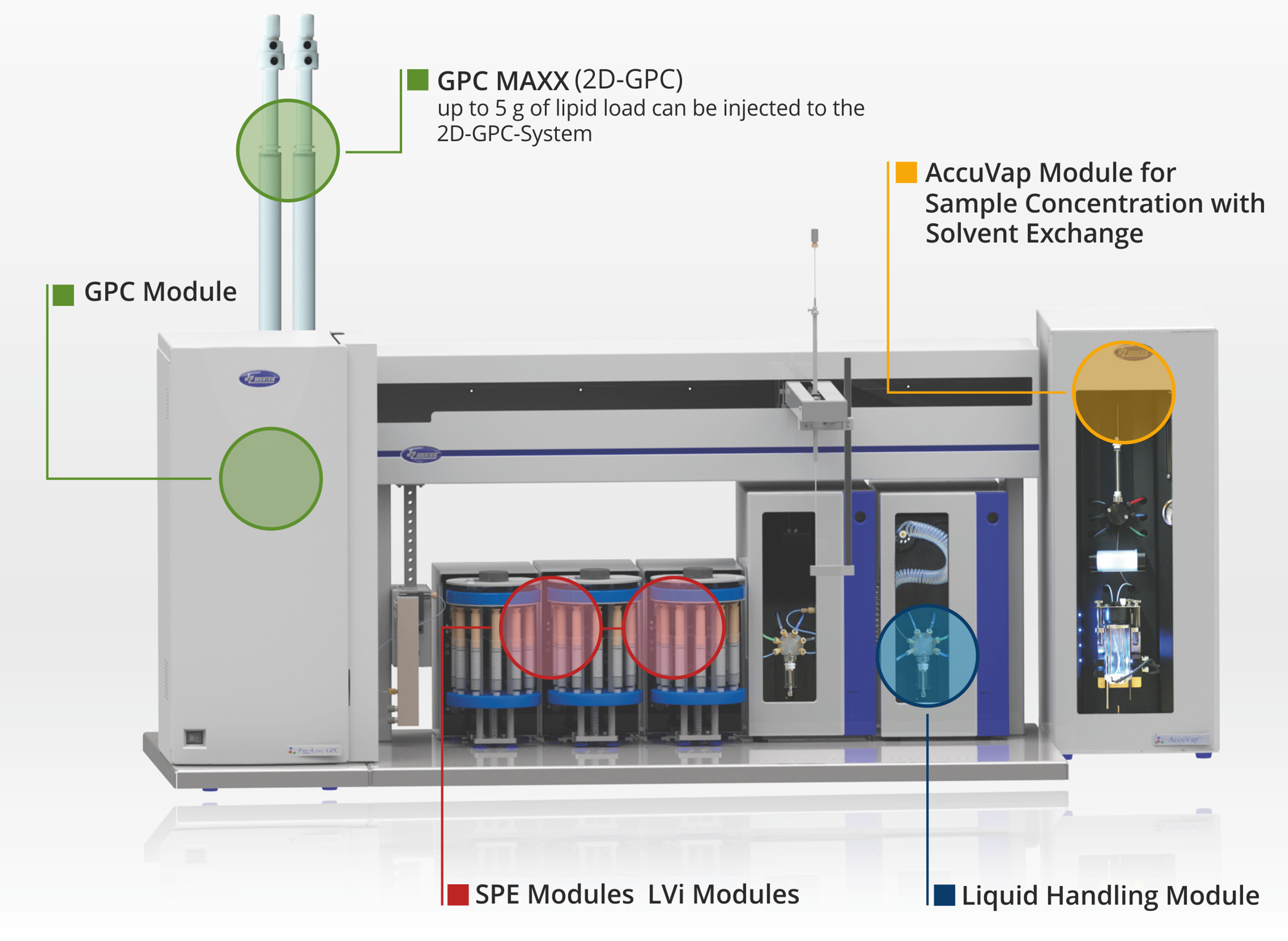
PrepLinc Module Options
Downloads
Application Notes
Application Note 105
Gel Permeation Chromatography is a size-exclusion liquid chromatography method used to remove lipids, sulfur and other co-extractives from environmental and food matrices prior to analytical analysis. It is a desirable technique because it is non-destructive and separates based on molecular size.
GPC Cleanup, while a beneficial cleanup technique, has been criticized for its solvent and time investments. GPC Cleanup using the traditional glass column requires one hour per sample and about 300mL of mobile phase solvent. Additionally, the traditional mobile phase is methylene chloride (DCM), a chlorinated solvent that requires expensive disposal.
To significantly decrease the cost of GPC Cleanup, the run time must be shortened. Simply increasing the mobile phase flow rate may speed the processing time, but will not decrease the amount of solvent used. It will also create pressure problems with the column. Another way to increase sample throughput while decreasing solvent consumption is to decrease the bed volume of the column. The lower bed volume will decrease the run time, thus decreasing the amount of solvent used to process each sample. There are, however, drawbacks to decreasing column bed length in some situations.
Please request your copy at J2 Scientific GmbH.
Application Note 110
The USDA FSIS National Residue Program mandates the testing of domestic meat to prevent violative levels of persistent pollutants like chlorinated pesticides from entering the food supply. Recent findings have prompted an interest in flame retardant levels in meat. Flame retardant compounds, like hexabromobiphenyl, are commonly found in flame retardants and enter the animal by ingestion of retardant-treated items. Little is known of the toxicity of fire retardant compounds in humans, but research in rodents suggests they are associated with cancer, endocrine disruption and brain impairment. Like chlorinated pesticides, fire retardant compounds are highly lipophilic and tend to accumulate in fatty tissue of animals in the food chain.
The standard method for determining chlorinated pesticide residue levels in meat employs GPC Cleanup with GC/ECD detection. In this study the flame retardant compound hexabromobiphenyl was simultaneously determined with a standard list of 20 chlorinated pesticides. Advances in GPC Cleanup column technology allows for a decrease in run time, keeping the entire procedure, extraction through analysis, close to 1 hour per sample.
Please request your copy at J2 Scientific GmbH.
Application Note 132
Currently, 12 substances are regulated by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) signed in May 2001 by 127 countries, and the work on finding new candidate chemicals to the convention has started. One group of substances in focus is polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). They are formed during all types of incomplete combustion of organic matter, and they exhibit the characteristic POPs properties: persistence, bio-accumulation, adverse effects and potential for long-range environmental transportation to a certain extent. Many of the PAHs are carcinogenic, they are also believed to exhibit reproductive effects, as well as immune system inhibiting properties, genotoxicity and mutagenicity.
The development of innovative analytical methods for determination of PAHs has been and is of fundamental importance, due to the high carcinogenicity of these compounds. The quali-quantitative analysis of PAHs is an important challenge due to the low concentration at which these hydrocarbons may be present.
Please request your copy at J2 Scientific GmbH.
Application Note 131
The use of Dietary Supplements by consumers has grown from <10% of the population to ~50% of the population over 10 years (US). Ginseng, one of the most popular botanical supplements, is a root crop requiring 4-7 years to mature. The long growing period increase the risk of fungal and insect attack. Numerous chlorinated pesticides, namely PCNB (Quintozene) and Tricyclazole are frequently found in ginseng samples. FDA & private laboratory testing revealed major contamination problems in the 1990’s which still persist today making residue monitoring a high priority. While many supplements can be routinely tested using modern techniques (QuEChERS), many chlorinated residues and high-lipid/saponin matrices can create challenges for this modern technique. Florisil column clean up (SPE) and Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) are utilized for such matrices. Historical GPC involved significant time and resources from the analyst to collect fractions, evaporate them and perform various solvent exchanges & SPE. Using the new-generation PrepLinc™ system, these functions are fully automated creating a ready-to-inject sample in an autosampler vial making GPC viable again for production laboratories. This poster (the first in a series) will introduce the system and briefly outline the methods utilized for sample preparation & provide matrix examples. Future posters/papers will provide further detail on the project.
Please request your copy at J2 Scientific GmbH.
Application Note 120
Extract purification for pico- or nanogram scale GC/MS is time consuming, laborious and costly, and may suffer from performance variations in manual cleanup chromatography. Size exclusion (GPC) followed by adsorptive chromatography is useful for cleanup of biota, soil and sediment extracts for high resolution PCDD/PCDF analyses. GPC cleanup of extracts is allowed or encouraged in several EPA methods and is of great value to laboratories practicing such analyses. Sample extract cleanup for PCDD./PCDF always involve a carbon column stage. Sample concentrate, typically after other cleanups, is passed onto carbon and forward elution drives out various interferences. Reverse elution utilizes solvent containing a component (e.g. toluene) having great affinity for carbon. This disgorges PCDD/PCDF congeners into an eluate ready for evaporation and analysis.
In this study GPC eluate was forward eluted through a carbon cartridge (bed of powder mixed with granular substrate, packed between two frits) placed in line after the GPC column. During forward elution, target compounds collect at or near the column head while interferences are flushed forward. Valve switching enables reverse elution with toluene for collection of targets. Thus PCDD/PCDF sample cleanup can be conducted in highly automated fashion with minimal operator contact.
Please request your copy at J2 Scientific GmbH.
Application Note 30
Chlorination of drinking water has been a commonly practiced method of disinfection for over a century. However, the disinfection by-products arising from the reaction of organic material in the water and chlorine may give rise to certain aberrant carcinogenic effects. EPA Method 552.1 and 552.3 prescribe procedures for testing of haloacid constituents in drinking water by ion-exchange or micro extraction, followed by esterification and quantitation by GC-ECD.
In this study, the 552.1 ion-exchange method is automated for different water samples to afford increased reproducibility, unattended operation, and consistency of sample loading and elution.
Please request your copy at J2 Scientific GmbH.
- Maximizing Lipid Load With 2-Dimensional GPC Cleanup
- QuEChERS, SPE and GPC: A Comparison of Sample Preparation Techniques for Analysis of Pesticides in Problematic Matrices
- Automated GPC with Inline SPE to Improve Sample Cleanup Without Adding Time or Solvent
- Additional cleanup for DIN EN 12393 minimising matrix effects and improving result quality in GC-MS
- A Combined SPE Method for Analysis of Chloroacetic Acids in Drinking Water
- Bestimmung von leichten und schweren polycyclischen aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffen (PAKs) in Fetten und Ölen pflanzlicher und tierischer Herkunft mittels automatisierter 2D-GPC und anschließender GC-MS-Detektion
- Automatisierte Probenvorbereitung für die Bestimmung von Pestizidrückständen in hocheffizienten Laboratorien mit GPC-GC-MS/MS und -LC-MS/MS
- Maximierte Probenaufgabe mit zweidimensionaler Gelpermeationschromatografie (2D-GPC)
- Automatisierung der Bausteine GPC, C1 und C2 der Methode L 00.00-34
- Cleanup-Methode für Nahrungsergänzungsmittel wie z.B. Ginseng
- Modifizierte Cleanup-Methode für Dioxine und persistente organische Schadstoffe (POPs)
- Automatisierung der Wasserextraktion mit dem SPE-Wasserextraktionssystem LVi
- Traditionelles Dioxin-Cleanup mit dem PrepLinc System
- Wiederauffindungsraten unterschiedlicher Pflanzenschutzmittel mit GPC und AccuVap
- Erfahrungen zur Automatisierung des GPC-Reinigungsver fahrens bei der Untersuchung von tierischen Lebensmitteln auf Chlorkohlenwasserstoffe
- Der Einsatz der automatischen Gelchromatographie zur Reinigung von Pesticidextrakten Organochlor
- Pflanzenbehandlungsmittel in Tabak und Tabakerzeugnissen
- Bestimmung der Fungizide Bitertanol, Fuberidazol, Imazalil, Rabenzazole, Triadimefon und Triadimenol in Pflanzen und Boden
- Methode zur Aufarbeitung von Lebensmitteln und Futtermitteln pflanzlicher und tierischer Herkunft für die Multirückstandsbestimmung lipoid- und wasserlöslicher Pflanzenbehandlungsmittel
- Zur Analytik von Chlorkohlenwasserstoffen in Zwiebeln nach Reinigung mit der Gelpermeationschromatographie
- Schnelle Untersuchung von Milch auf chlorierte Kohlenwasserstoffe mittels automatischer Gelchromatographie
- Automatisierte Gelchromatographie als Reinigungsverfahren zum Nachweis von ECD-erfaßbaren Wirkstoffen, chlorierten Kohlenwasserstoffen, Pentachlorphenol sowie von Diphenyl und o-Phenylphenol in pflanzlichen Materialien
- Untersuchungen zum Einsatz der Gelpermeationschromatograpie in der Rückstandsanalytik
- Nachweis von Aflatoxin B1 in Futtermitteln für Milchtiere
- Bestimmung der Rückstände von aromatischen Dinitroverbindungen mittels gelchromatischer Reinigung
- Die Gelpermeationschromatographie, eine universelle Reinigungsmethode in der Analytik von Pflanzenschutzmitteln
- Untersuchungen zur Messung und Bewertung von Rückständen des Ektoparasitenbekämpfungsmittels Phoxim in Milch
- Methode zur Aufarbeitung von Lebensmitteln und Futtermitteln pflanzlicher und tierischer Herkunft für die
- Multirückstandsbestimmung lipoid- und wasserlöslicher Pflanzenbehandlungsmittel
- Untersuchungen zur Gelchromatograpie (GPC) als Reinigungsverfahren in der Rückstandsanalytik von Tierarzneimitteln
- Eine schnelle Methode zur Bestimmung des Ebergeruchsteroids Androstenon
- Analysenverfahren zur Bestimmung von polychlorierten Dibenzodioxinen und Dibenzofuranen in Frauenmilch
- Untersuchungen zum Vorkommen von Moschus-Xylol in Fischen
- GPC-clean up von fetthaltigen Matrizes in der Rückstandsanalytik unter Verwendung von OPTIMA-Säulen
- Entwicklung einer Methode zur Bestimmung von Nitromoschusverbindungen im Hausstaub
Contact
J2 Scientific GmbH
Reifenstuelstraße 3
80469 Munich / Germany
Tel.: +49 (0) 89 72069587
E-Mail: info@j2scientific.eu
Distributor
ANTEC GmbH
Analysen- und Prozesstechnik
Hauptstraße 4
82404 Sindelsdorf
Tel.: +49 (0) 8856 9910



